Abstract
Background:
CD20 antibody-based chemotherapy has been verified as a valid strategy and prolonged the overall survival (OS) of CD20(+) B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (B-NHL) patients. However, over 40% of these patients finally would be relapsed or refractory(R/R) to CD20 antibody rituximab. Treatment of these R/R B-NHL patients has not been standardized yet. Furthermore, it is still a question that whether CD20-specific CAR T-cells could provide an alternative therapy in rituximab-relapsed/refractory B-NHL patients.
Methods:
Here, we conducted a prospective single-center study on patients with relapsed/refractory to CD20 antibody(No.ChiCTR2000036350). The aim of this study aims was to evaluate the efficacy and in vivo persistence of CART-20 cells in subjects with rituximab R/R CD20(+) B-NHL patients. Between October 2017 to December 2020, 15 patients with R/R B-NHL patients (including 14 DLBCL patents and 1 MCL patient) received anti-CD20 specific CAR T cell therapy. The efficacy of CAR T-cells therapy was evaluated at different assessment points by CT scan or 18FDG-PET. CAR-T expansion in blood was monitored regularly by real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR).
Results:
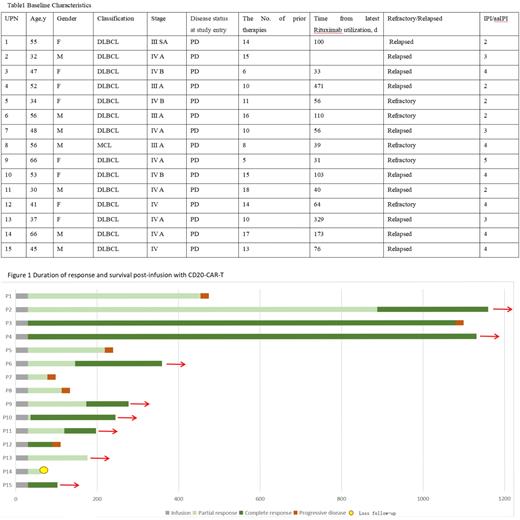
In this study, the clinical characteristic of these enrolled patients was a median age at 48 years (range 30 to 66), male n=7(47%). 10 (67%) patients were relapsed and 5 patients (33%) were refractory to rituximab-based chemotherapy.(Table 1) All of these patients were at advanced stage III/IV and 7 (47%) of them were diagnosed with bulky disease. The median time from latest rituximab utilization is 70 days (rang 31-471 days) before CAR T-20 cells infusion. The median number of lines of previous treatments was 4 (2-8). 14 patients (93%) received CAR T-20 with a dose of 1*10^7/kg, the median follow-up time for patients was 219 days (32 to 1231). CRS (100%) was observed in all 15 infusion patients: 11 patients grade I-II and 4 patients' grade ≥III. ICANS was recorded only in 1 patient (grade I). At 30 days after the infusion, the clinical response of all 15 infusion patients could be assessed: 4 (27%) CR, 11 (73%) PR, and ORR 100%.(Figure 1) 5 patients who were in PR at 30 days converted to CR, with a median time of 116 (6-858), and continued follow-up without relapse; 6 patients (40%) had relapse, with a median relapse time of 136 days (48- 1050), this might be related to the short time of rituximab before the CAR-T infusion.Although the cases are limited, we can still draw a preliminary conclusion that the use of rituximab within three months may not affect the efficacy of CD20-CAR-T, but may lead to early recurrence. Furthermore, the persistence time of CART-20 cells were comparably longer than that CART-19 cell infusions.
Conclusions:
In conclusion,these findings suggest that the use of CAR T-20 can be served as a salvage therapy in Rituximab-refractory CD20(+) B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma and raises the possibility of using CAR T-20 in an early disease stage.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal